Strep Throat: How to Get Diagnosed, Which Antibiotics Work, and What to Expect During Recovery
Nov 21 2025
When you reach for ibuprofen or naproxen to ease a headache, sore muscles, or menstrual cramps, you’re using a NSAIDs, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that reduce pain, fever, and inflammation by blocking enzymes in the body. Also known as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories, these drugs are among the most widely used medications worldwide — but they’re far from harmless.
NSAIDs work by targeting COX enzymes, which produce prostaglandins — chemicals that trigger pain and swelling. That’s why they help with arthritis, sprains, and even fevers. But those same prostaglandins also protect your stomach lining and support kidney function. When you block them too much, or for too long, you risk ulcers, bleeding, or kidney damage. And if you’re on blood thinners, antidepressants, or high blood pressure meds, NSAIDs can make those drugs less effective — or more dangerous. This isn’t theoretical. Studies show over 100,000 hospitalizations each year in the U.S. are linked to NSAID complications.
Not all NSAIDs are the same. Some, like aspirin, also thin your blood — useful for heart protection but risky if you’re prone to bleeding. Others, like celecoxib, were designed to be gentler on the stomach, but still carry heart risks. And while people often confuse NSAID side effects with allergies, true allergic reactions are rare. More common? Intolerance — nausea, dizziness, or swelling that builds up over time. If you’ve ever been told you’re "allergic" to ibuprofen but can take naproxen fine, you’re likely dealing with intolerance, not an immune response. That distinction matters because mislabeling can keep you from getting effective pain relief.
NSAIDs also interact with other common treatments. If you’re taking steroids for inflammation, or diuretics for fluid retention, combining them with NSAIDs can strain your kidneys. Even something as simple as a daily aspirin for heart health can turn risky if you start popping extra ibuprofen for back pain. And if you have GERD, osteoporosis, or are on HIV or TB meds, NSAIDs might not be the best choice at all.
Below, you’ll find real-world guides on how NSAIDs fit into broader medication use — from spotting the difference between side effects and true allergies, to understanding how they clash with other drugs like bisphosphonates, rifampin, or antivirals. These aren’t abstract warnings. They’re lessons from people who’ve been there — and what they learned the hard way.
Learn how NSAIDs, acetaminophen, and antihistamines work, their risks, and how to choose the right OTC pain, fever, or allergy relief safely. Avoid common mistakes that lead to overdoses and side effects.

Nov 21 2025

Oct 27 2025
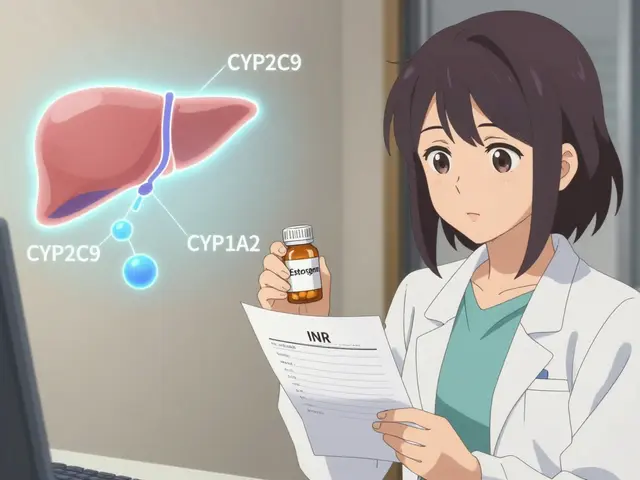
Feb 7 2026
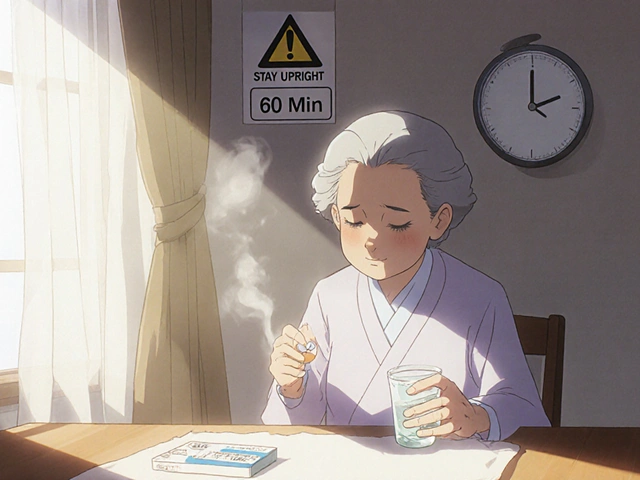
Nov 22 2025

Oct 16 2025