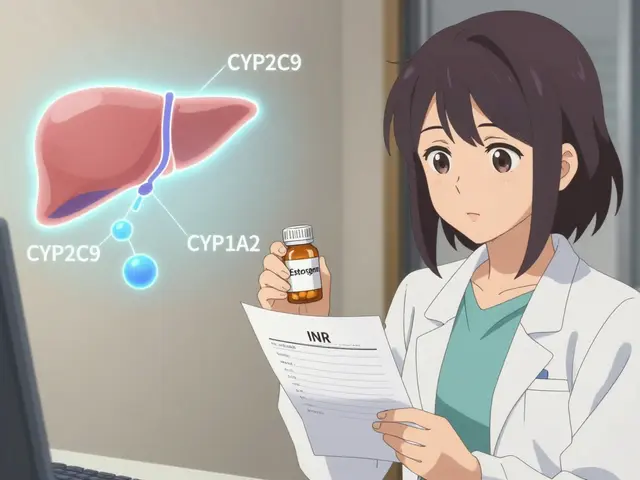
Estrogen Interactions with Warfarin: What You Need to Know About Blood Thinners and Hormones
Feb 7 2026
Antioxidants are the body’s built‑in defenders against damage from tiny molecules called free radicals. When free radicals build up, they can hurt cells and speed up aging or disease. Antioxidants trap those troublemakers, keeping your cells healthier for longer.
Think of antioxidants as tiny cleaners that mop up oxidative stress. They work in your blood, skin, and even inside each cell. By neutralizing free radicals, antioxidants help lower the risk of heart problems, support immune function, and protect skin from premature wrinkles. The science shows that a diet rich in antioxidants can improve recovery after exercise and may ease inflammation.
Most of the best antioxidant foods are easy to find at any grocery store. Berries – especially blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries – pack a punch. Dark leafy greens like spinach and kale also score high. Nuts such as almonds and walnuts add a crunchy boost, while seeds (flax, chia, pumpkin) bring extra fiber and healthy fats.
Don’t forget drinks. Green tea, black tea, and coffee each deliver antioxidants called polyphenols. If you like something sweet, a small piece of dark chocolate (70% cocoa or more) can satisfy cravings while giving you a dose of flavonoids.
When you’re short on time, a quick smoothie can sneak in several sources at once. Blend a handful of frozen berries, a scoop of plain Greek yogurt, a spoonful of chia seeds, and a splash of almond milk. You’ll get a mix of vitamin C, vitamin E, and plant‑based compounds without any extra prep.
If you prefer a supplement, look for products that list specific antioxidants like vitamin C, vitamin E, selenium, or coenzyme Q10. Make sure the brand tests for purity and follows Good Manufacturing Practices. Supplements can help fill gaps, but they’re not a replacement for whole foods.
Here are three easy habits to up your antioxidant intake:
Most people can safely add antioxidants through food without any side effects. However, high doses of certain supplements (like vitamin E or beta‑carotene) can interact with medications or cause issues for people with specific health conditions. Always check with a pharmacist or doctor if you’re on blood thinners, cholesterol meds, or have a thyroid disorder.
Bottom line: antioxidants are a simple, tasty way to support overall health. By choosing a variety of colorful fruits, vegetables, nuts, and teas, you give your body the tools it needs to fight oxidative stress every day.
Clear, evidence-backed guide to vitamin E supplements for skin glow and health. Learn benefits, safe dosage, how to choose, and how to pair with your routine.
Feb 7 2026

Jan 22 2026

Dec 20 2025

Jan 9 2026

Nov 25 2025